Overview

Basically, fallen arches refers to a flattening of the feet that takes place in adulthood. Although there may be other causes, this flattening usually occurs when the tendon (posterior tibial tendon) and ligaments that hold the arch in place gradually stretch. As we get older and our cumulative use of these tendons and ligaments increases, they lose their ability to maintain that nice arch shape, and may even begin to tear. This stretching or tearing may also be the result of an injury, obesity, or a genetic predisposition for flat feet.
Causes
Footwear: shoes which limit toe movement; high heels. Barefoot walking may be protective. A tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles (heel cord contracture). This may help to cause Pes Planus, or may contribute to symptoms such as foot pain when there is existing Pes Planus. Obesity. Other bony abnormalities, eg rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, coalition (fusion) of tarsal bones, equinus deformity. Ligamentous laxity, eg familial, Marfan's syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Down's syndrome. Other factors causing foot pronation, eg hip abductor weakness and genu valgum.
Symptoms
Not everyone who has flat feet experiences symptoms. Others, however, feel persistent pain in their feet and wearing shoes can prove additionally painful. Others only feel symptoms when they walk more than normal, go jogging or participate in a sport that involves running or kicking.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatment is simple for flat feet. We will carry out a biomechanical assessment and full history, often along side a Computerised Gait Scan to give us an idea of how the foot is compensating. Treatment will be to, control how the foot hits the ground, support the middle of the foot and prevent the arch collapsing, promote normal movement in the front of the foot. The ability to do this will be dictated by the movement within the foot to start with. Treatment for all the above problems are often combined with a physiotherapy session in order to help develop a stretching and strengthening program for the back of the legs and the pelvis in order to allow normal function when the orthoses have been prescribed. If you are born with flat feet you will not grow out of them - if you get orthoses, like glasses you will need them for the rest of your life if you want to correct the mechanics in your foot. In 95% of cases, orthoses will reduce symptoms by at least 85%. In the other 5% we will work with them to get them to this level.
Surgical Treatment

Since there are many different causes of flatfoot, the types of flatfoot reconstruction surgery are best categorized by the conditions. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. In this condition, the tendon connecting the calf muscle to the inner foot is torn or inflamed. Once the tendon is damaged it no longer can serve its main function of supporting the arch of the foot. Flatfoot is the main result of this type of condition and can be treated by the following flatfoot reconstruction surgeries. Lengthening of the Achilles tendon. Otherwise known as gastrocnemius recession, this procedure is used to lengthen the calf muscles in the leg. This surgery treats flatfoot and prevents it from returning in the future. This procedure is often combined with other surgeries to correct posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Cleaning the tendon. Also known as tenosynovectomy, this procedure is used in the earlier and less severe stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. It is performed before the arch collapses and while the tendon is only mildly affected. The inflamed tissue is cleaned away and removed from the remaining healthy tendon. Tendon transfer. This procedure is done to correct flatfoot and reform the lost arch in the foot. During the procedure, the diseased tendon is removed and replaced by tendon from another area of the foot. If the tendon is only partially damaged, the inflamed part is cleaned and removed then attached to a new tendon. Cutting and shifting bones. Also called an osteotomy, this procedure consists of cutting and reconstructing bones in the foot to reconstruct the arch. The heel bone and the midfoot are most likely reshaped to achieve this desired result. A bone graft may be used to fuse the bones or to lengthen the outside of the foot. Temporary instrumentation such as screws and plates can also be used to hold the bones together while they heal.

Basically, fallen arches refers to a flattening of the feet that takes place in adulthood. Although there may be other causes, this flattening usually occurs when the tendon (posterior tibial tendon) and ligaments that hold the arch in place gradually stretch. As we get older and our cumulative use of these tendons and ligaments increases, they lose their ability to maintain that nice arch shape, and may even begin to tear. This stretching or tearing may also be the result of an injury, obesity, or a genetic predisposition for flat feet.
Causes
Footwear: shoes which limit toe movement; high heels. Barefoot walking may be protective. A tight Achilles tendon or calf muscles (heel cord contracture). This may help to cause Pes Planus, or may contribute to symptoms such as foot pain when there is existing Pes Planus. Obesity. Other bony abnormalities, eg rotational deformities, tibial abnormalities, coalition (fusion) of tarsal bones, equinus deformity. Ligamentous laxity, eg familial, Marfan's syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Down's syndrome. Other factors causing foot pronation, eg hip abductor weakness and genu valgum.
Symptoms
Not everyone who has flat feet experiences symptoms. Others, however, feel persistent pain in their feet and wearing shoes can prove additionally painful. Others only feel symptoms when they walk more than normal, go jogging or participate in a sport that involves running or kicking.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
best arch support insoles for plantar fasciitis
Non Surgical Treatment
The treatment is simple for flat feet. We will carry out a biomechanical assessment and full history, often along side a Computerised Gait Scan to give us an idea of how the foot is compensating. Treatment will be to, control how the foot hits the ground, support the middle of the foot and prevent the arch collapsing, promote normal movement in the front of the foot. The ability to do this will be dictated by the movement within the foot to start with. Treatment for all the above problems are often combined with a physiotherapy session in order to help develop a stretching and strengthening program for the back of the legs and the pelvis in order to allow normal function when the orthoses have been prescribed. If you are born with flat feet you will not grow out of them - if you get orthoses, like glasses you will need them for the rest of your life if you want to correct the mechanics in your foot. In 95% of cases, orthoses will reduce symptoms by at least 85%. In the other 5% we will work with them to get them to this level.
Surgical Treatment

Since there are many different causes of flatfoot, the types of flatfoot reconstruction surgery are best categorized by the conditions. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. In this condition, the tendon connecting the calf muscle to the inner foot is torn or inflamed. Once the tendon is damaged it no longer can serve its main function of supporting the arch of the foot. Flatfoot is the main result of this type of condition and can be treated by the following flatfoot reconstruction surgeries. Lengthening of the Achilles tendon. Otherwise known as gastrocnemius recession, this procedure is used to lengthen the calf muscles in the leg. This surgery treats flatfoot and prevents it from returning in the future. This procedure is often combined with other surgeries to correct posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Cleaning the tendon. Also known as tenosynovectomy, this procedure is used in the earlier and less severe stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. It is performed before the arch collapses and while the tendon is only mildly affected. The inflamed tissue is cleaned away and removed from the remaining healthy tendon. Tendon transfer. This procedure is done to correct flatfoot and reform the lost arch in the foot. During the procedure, the diseased tendon is removed and replaced by tendon from another area of the foot. If the tendon is only partially damaged, the inflamed part is cleaned and removed then attached to a new tendon. Cutting and shifting bones. Also called an osteotomy, this procedure consists of cutting and reconstructing bones in the foot to reconstruct the arch. The heel bone and the midfoot are most likely reshaped to achieve this desired result. A bone graft may be used to fuse the bones or to lengthen the outside of the foot. Temporary instrumentation such as screws and plates can also be used to hold the bones together while they heal.


.jpg)
 Morton neuromas are focal areas of symptomatic perineural fibrosis around a plantar digital nerve of the foot. The abnormality is non-neoplastic and does not represent a true neuroma. It may more correctly be known as Morton?s metatarsalgia. The condition is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament. It most often occurs in middle-aged individuals and is many times more common in women than men. Approximately 30% of asymptomatic middle-aged persons have the radiological pathologic findings of a Morton?s neuroma.
Morton neuromas are focal areas of symptomatic perineural fibrosis around a plantar digital nerve of the foot. The abnormality is non-neoplastic and does not represent a true neuroma. It may more correctly be known as Morton?s metatarsalgia. The condition is thought to be due to chronic entrapment of the nerve by the intermetatarsal ligament. It most often occurs in middle-aged individuals and is many times more common in women than men. Approximately 30% of asymptomatic middle-aged persons have the radiological pathologic findings of a Morton?s neuroma.






 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms A bunion is a bone deformity caused by an enlargement of the joint at the base and side of the big toe ( metatarsophalangeal joint ). Bunions form when the toe moves out of place. The enlargement and its protuberance cause friction and pressure as they rub against footwear. The growing enlargement or protuberance then causes more irritation or inflammation. In some cases, the big toe moves toward the second toe and rotates or twists, which is known as Hallux Abducto Valgus. Bunions can also lead to other toe deformities, such as hammertoe.
A bunion is a bone deformity caused by an enlargement of the joint at the base and side of the big toe ( metatarsophalangeal joint ). Bunions form when the toe moves out of place. The enlargement and its protuberance cause friction and pressure as they rub against footwear. The growing enlargement or protuberance then causes more irritation or inflammation. In some cases, the big toe moves toward the second toe and rotates or twists, which is known as Hallux Abducto Valgus. Bunions can also lead to other toe deformities, such as hammertoe.
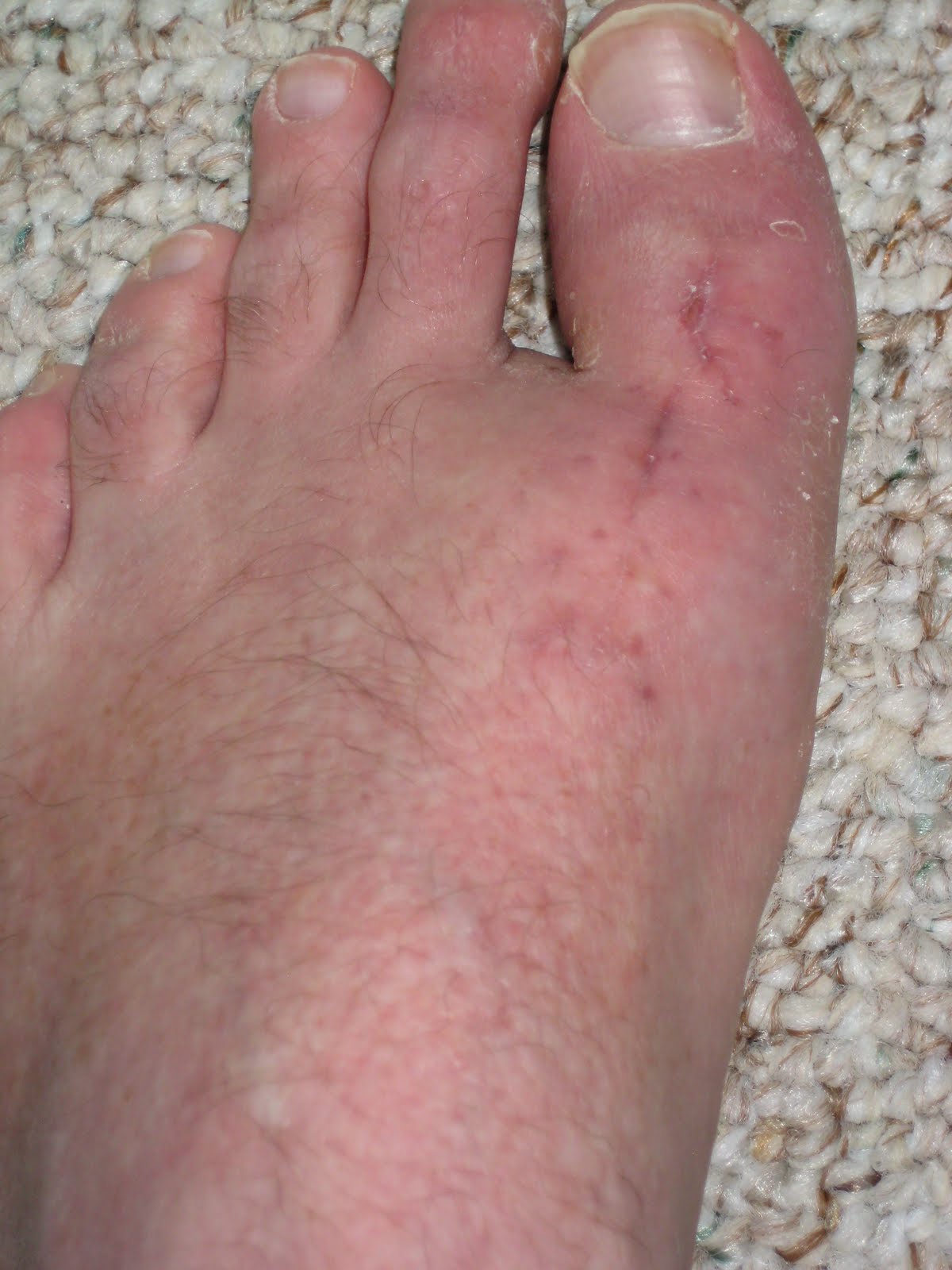
 A bunion is an enlargement of bone or tissue around the joint at the base of the big toe. The big toe may turn toward the second toe. The tissues around the joint may be swollen and tender. A bony bump at the base of the little toe is called a bunionette or tailor's bunion. The little toe also bends inward, and the joint swells or enlarges.
A bunion is an enlargement of bone or tissue around the joint at the base of the big toe. The big toe may turn toward the second toe. The tissues around the joint may be swollen and tender. A bony bump at the base of the little toe is called a bunionette or tailor's bunion. The little toe also bends inward, and the joint swells or enlarges.
